How Far Does Sound Travel: The Science of Acoustics
Do you ever stop to think about how sound travels? It’s an interesting phenomenon that occurs everyday and yet we often take it for granted. In this blog post, we will explore the science of acoustics and how sound travels. We will answer the question of how far sound can travel and how it is affected by different factors. Stay tuned for an in-depth look at this fascinating topic!

Nature Of Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through some medium, such as air or water. Sound can propagate through solids and liquids better than gases because the density and stiffness are greater. So how far does sound travel? In this article we will answer how sound travels and how to calculate how far it travels in different scenarios.
Sound Transmits Conception
A common misconception with regard to how sound transmits itself between two points (for example from speaker to ear) is that the source creates waves of compression in the surrounding gas which then proceed on their way at a constant speed until they strike something else; either another solid object or our ears. This analogy might be okay for describing what goes on at low frequencies but once we go beyond around 1000 Hz, the propagation of sound becomes far more complex.
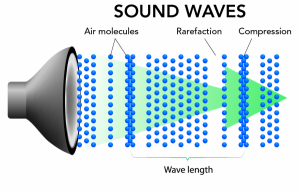
At low frequencies (below around 1000 Hz), sound waves tend to travel in all directions more or less equally and bounce off objects like a rubber ball would. As frequency increases however, the directivity of sound increases as well. So high-frequency sounds are more likely to travel in a straight line between two points than low frequencies. This is why we can often hear someone calling from some distance away when there is loud music playing – because the higher frequencies carry further than the lower ones.
How Far Can Sound Travel
There are three ways that sound can be transmitted: through air, through water, or through solids. The speed of sound through each medium is different and depends on the density and stiffness of the material.
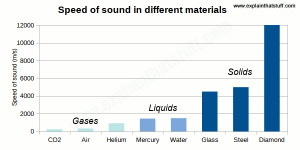
The speed of sound through air is about 343 m/s (or 760 mph), and it travels faster in warmer air than colder air. The speed of sound through water is about 1500 m/s, and it travels faster in salt water than fresh water. The speed of sound through solids is much faster than through either gases or liquids – about 5000-15000 m/s. This is why we can often hear someone coming before we see them – the sound waves are travelling through the solid ground to our ears!
Now that we know how sound propagates and how its speed depends on the medium, let’s take a look at how to calculate how far it will travel between two points. We can use the equation
distance = speed x time
For example, if we want to know how far a sound will travel in one second, we have:
distance = 343 m/s x 0.001 s = 343 m
So sound travels 1 kilometer in roughly 3 seconds and 1 mile in roughly 5 seconds.
Does Вecibel Level affect the Sound Distance?
The surface area around a sound source’s location grows with the square of the distance from the source. This implies that the same amount of sound energy is dispersed over a larger surface, and that the energy intensity decreases as the square of the distance from the source (Inverse Square Law).
Experts of Acoustical control says, that
For every doubling of distance, the sound level reduces by 6 decibels (dB), (e.g. moving from 10 to 20 metres away from a sound source). But the next 6dB reduction means moving from 20 to 40 metres, then from 40 to 80 metres for a further 6dB reduction.
How Far Can Sound Travel In Real World
In real world, there are many factors that can affect how far a sound travels. Factors such as air density, temperature and humidity have an impact on its propagation; obstacles like buildings or mountains could also block some frequencies from going through while letting others pass (this happens because at high frequencies they behave more like waves).
Sounds can propagate through solids better than they can propagate through air because their density/stiffness are greater (this means that sound travels faster). In addition to this, we also know that it takes less time for a high frequency wave to reach us from its source compared with low frequencies. For example if there’s some kind of obstacle blocking our path then it might take longer for waves at higher frequencies than those below 1000 Hz to past them.
FAQs
Can Sound Waves Travel Infinitely?
No. The higher the frequency of a sound wave, the shorter its wavelength becomes. As wavelength decreases, the amount of energy in a sound wave also decreases and eventually it dissipates completely. This is why we often can’t hear someone calling from very far away when there’s loud music playing – because the high frequencies are being blocked out by all the noise!
Can Sound Travel 20 Miles?
The air may be permeable to these lower-frequency, sub-audible sound waves generated by elephants. Some whale species’ frequencies might travel through seawater for 1500 kilometers or 900 miles.
How Far Can a Human Scream Travel?
The normal intelligible outdoor range of the male human voice in still air is 180 m (590 ft 6.6 in).

The Guiness World Record of the Farthest distance travelled by a human voice belongs the Spanish-speaking inhabitants of the Canary Island of La Gomera, is intelligible under ideal conditions at 8 km (5 miles).
In Conclusion
At the end of this blog post, you should have a better understanding of how sound travel and what factors affect it. If you want to learn more about acoustics and sounds, you can check out our resources here.